Which Is Not Required For A Reflex Arc: Unveiling Essential Components
What Is A Reflex Arc | Physiology | Biology | Fuseschool
Keywords searched by users: Which Is Not Required For A Reflex Arc which reflex has a contralateral component?, which of the following is not required for a reflex arc, reflex arc is formed by, which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc, which reflex requires gamma motor neurons to set the length of the muscle?, classify the neuron at a., art-based question: pns, question 1, which of the following is the correct simple spinal reflex arc?
What Is Not Involved In A Reflex Arc?
A reflex arc is a neural pathway responsible for rapidly transmitting information from sensory receptors to effectors, typically through the spinal cord. Importantly, the reflex arc functions independently of conscious thought, making it a crucial mechanism for swift and automatic responses to stimuli. Unlike other neural processes, such as voluntary actions and cognitive functions, the brain is notably not directly involved in the reflex arc. Instead, this pathway is primarily confined to the spinal cord and associated neural structures, allowing for rapid and involuntary reactions to various stimuli without requiring conscious processing by the brain.
What Is Required For A Reflex Arc?
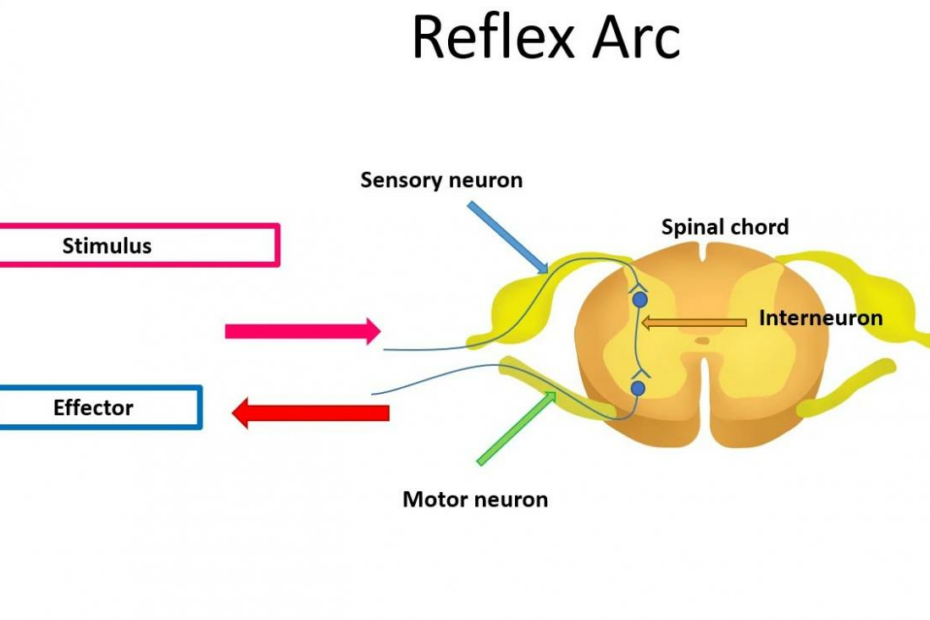
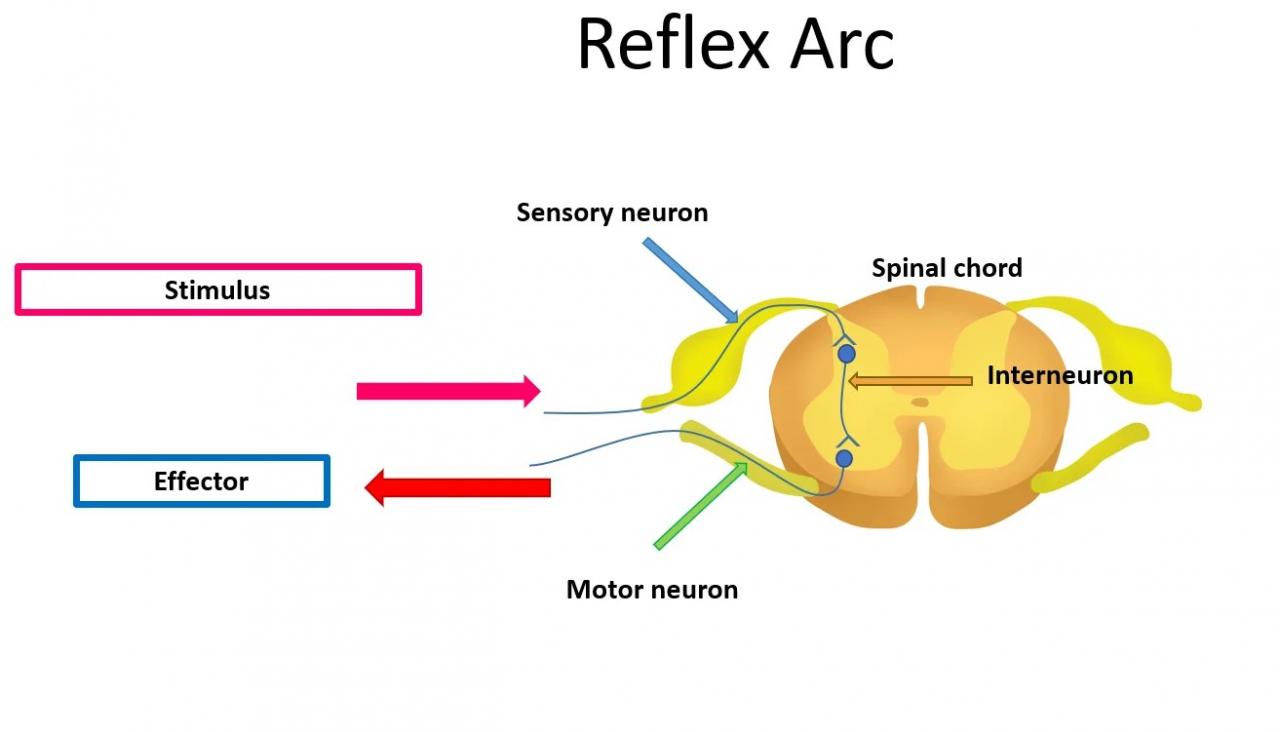
A reflex arc, the fundamental component of our body’s rapid response system, requires a specific arrangement involving three essential elements: a receptor, an interneuron (also known as an adjustor), and an effector. These three components work in unison to create a functional unit capable of swift and automatic reactions to various stimuli.
To begin, sensory cells play a pivotal role by transmitting incoming information, referred to as afferent impulses, from the receptor to a central interneuron. This central interneuron serves as a vital connection point, facilitating communication with a motor neuron. This intricate network ensures that the reflex arc can efficiently process and transmit signals, enabling rapid responses to a wide range of sensory stimuli.
Which 3 Are Involved In A Reflex Arc?
A reflex arc involves a series of coordinated actions within the nervous system that allow the body to respond rapidly to stimuli without conscious thought. There are three key components involved in a reflex arc:
-
Sensory Neuron: This specialized nerve cell is responsible for detecting a stimulus, such as touching a hot object. When activated, it rapidly sends electrical impulses or signals to other parts of the nervous system.
-
Relay Neuron (Interneuron): The relay neuron plays a crucial role in the reflex arc by transmitting signals from the sensory neuron to the motor neuron. These relay neurons are typically located in the spinal cord, which is part of the Central Nervous System (CNS).
-
Motor Neuron: Once the relay neuron receives the signal, it then passes it on to the motor neuron. Motor neurons carry the electrical impulses from the relay neuron to the effector.
-
Effector: The effector is usually a muscle or gland that carries out the response to the stimulus. In the case of a hot object, the effector could be a muscle that contracts to move the hand away from the source of heat.
In summary, a reflex arc involves these three crucial components: the sensory neuron, the relay neuron (found in the CNS), and the motor neuron, along with the effector, working together to produce a rapid and involuntary response to a stimulus.
Details 43 Which Is Not Required For A Reflex Arc






Categories: Share 57 Which Is Not Required For A Reflex Arc
See more here: chinhphucnang.com

Learn more about the topic Which Is Not Required For A Reflex Arc.
- Which of the following is NOT required for a reflex arc? A
- A reflex arc does not involve | Biology Questions – Toppr
- Reflex arc | Description & Components – Britannica
- Reflex arc – How does the nervous system help us respond? – BBC
- Muscle Stretch Reflex – Reflex Arc Components – TeachMePhysiology
- reflexes Flashcards | Quizlet
See more: blog https://chinhphucnang.com/dealbook